Similar
A companion to Blackie's tropical readers, books I and II - containing suggestions for experiemnts and practical work (1911) (14586016389)
Summary
Identifier: companiontoblack00wort (find matches)
Title: A companion to Blackie's tropical readers, books I and II : containing suggestions for experiemnts and practical work
Year: 1911 (1910s)
Authors: Wortley, E. J
Subjects: Nature study -- Juvenile literature Natural history -- Tropics Natural history -- Jamaica
Publisher: Glasgow Bombay : Blackie
Contributing Library: The LuEsther T Mertz Library, the New York Botanical Garden
Digitizing Sponsor: The LuEsther T Mertz Library, the New York Botanical Garden
Text Appearing Before Image:
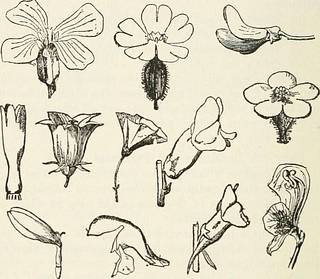
that leaf now gets wet. Expt. 39. Deciduous and Persistent Leaves. (a) Whenever you observe a plant bare of leaves (e.g.red plum, cedar, genip, silk-cotton) record its name, to-gether with a note of the time of the year at which itregularly sheds its leaves. (b) Make a list of twelve trees that do not shed alltheir leaves at regular seasons, e.g. lignum-vita?, mango,lime, bread-fruit, sweet-sop. Expt. 40. General Collection. — Make a large andgeneral collection of leaves, and sort them into thefollowing classes:— (a) Simple and compound leaves. (b) Undivided simple and lobed simple leaves. (c) Parallel- and net-veined leaves. 42 COMPANION TO TROPICAL READERS Expt. 41. Full Description of Leaves.—Draw any three leaves, describing the nature of the various parts(shape, petiole, veins, margin, &c). FLOWERS—I, II, and III (See Tropical Readers, Book I, pp. 93-101.) Expt. 42. Description of Flower.—Collect and describethe different parts of three flowers, e.g. orange, guava.
Text Appearing After Image:
Fig. 19.—Forms of Corolla Expt. 43. Drawings.—Make careful drawings of anythree flowers, naming the various parts. Expt. 44. United Petals.—Collect twelve flowers inwhich the petals are more or less united, giving the EXPERIMENTS AND PRACTICAL WORK 43 flower the shape of a bell, funnel, &c. (fig. 19), e.g.guava, orange. Expt. 45. Sepals.—Collect twelve flowers with greensepals and four with coloured sepals, e.g. poinciana,orchids. Expt. 46. Number of Petals. — Observe and recordthe number of petals usually found in— (a) Monocotyledonous plants, e.g. red lily, ginger lily. (b) Dicotyledonous plants, e.g. hibiscus, orange. Expt. 47. Insect - pollinated Flowers. — Examineflowers that are visited by bees (e.g. logwood, genip,lignum-vitae); look for the sweet liquid (nectar) andtaste it. Expt. 48. Pollen found on Stamens of Flowers.—Examine four fully opened flowers, and see if you canget pollen from the stamens to adhere to your finger. FRUITS (See Tropical Readers, Bo
Tags
Date
Source
Copyright info






















