Similar
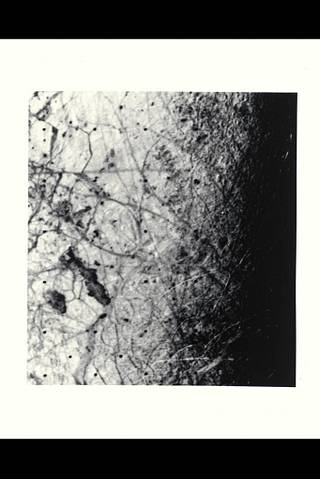
Range : 225,000 kilometers (140,625 miles) This image of the Jovian moon Europa was taken by Voyager 2 along the evening terminator, which best shows the surface topography of complex narrow ridges, seen as curved bright streaks, 5 to 10 kilometers wide, and typically 100 kilometers in length. The area shown is about 600 by 800 kilometers, and the smallest features visible are about 4 kilometers in size. Also visable are dark bands, more diffused in character, 20 to 40 kilometers wide and hundreds to thousands of kilometers in length. A few features are suggestive of impact craters but are rare, indication that the surface thought to be dominantly ice is still active, perhaps warmed by tidal heating like Io. The larger icy satellites, Callisto and Ganymede, are evidently colder with much more rigid crusts and ancient impact craters. The complex intersection of dark markings and bright ridges suggest that the surface has been fractured and material from beneath has welled up to fill the cracks. ARC-1979-A79-7093
Summary
Range : 225,000 kilometers (140,625 miles) This image of the Jovian moon Europa was taken by Voyager 2 along the evening terminator, which best shows the surface topography of complex narrow ridges, seen as curved bright streaks, 5 to 10 kilometers wide, and typically 100 kilometers in length. The area shown is about 600 by 800 kilometers, and the smallest features visible are about 4 kilometers in size. Also visable are dark bands, more diffused in character, 20 to 40 kilometers wide and hundreds to thousands of kilometers in length. A few features are suggestive of impact craters but are rare, indication that the surface thought to be dominantly ice is still active, perhaps warmed by tidal heating like Io. The larger icy satellites, Callisto and Ganymede, are evidently colder with much more rigid crusts and ancient impact craters. The complex intersection of dark markings and bright ridges suggest that the surface has been fractured and material from beneath has welled up to fill the cracks.
In 1977, Voyager 1 and 2 started their one-way journey to the end of the solar system and beyond, now traveling a million miles a day. Jimmy Carter was president when NASA launched two probes from Cape Canaveral. Voyager 1 and its twin, Voyager 2, were initially meant to explore Jupiter, Saturn, and their moons. They did that. But then they kept going at a rate of 35,000 miles per hour. Each craft bears an object that is a record, both dubbed the Golden Records. They were the product of Carl Sagan and his team who produced a record that would, if discovered by aliens, represent humanity and "communicate a story of our world to extraterrestrials."
Tags
Date
Source
Copyright info




![[Groups of stars]. Book illustration from Library of Congress [Groups of stars]. Book illustration from Library of Congress](https://cache.getarchive.net/Prod/thumb/cdn4/L3Bob3RvLzE3NTAvMDEvMDEvZ3JvdXBzLW9mLXN0YXJzLTY0MC5qcGc%3D/40/39/jpg)











































