Similar
Abraham van den Broeck - Korte beschryvinge van de landschappen des werelts enz.
Summary
Scales vary.
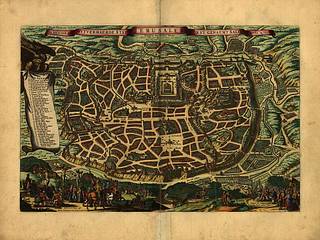
Title from leather label on cover.
Label has monogram E. B. de V., surmounted by a crown.
Maps, not dated, intended to be bound in a Bible, but assembled in a modern half Morocco binding.
The maps have privileges, not dated, for 15 years, granted to N. Visscher by the states of Holland and West Friesland.
Maps 3, 4, and [5] each have engraved signature: C. J. Visscher excud.: maps 2, 3, [5] and [6]: Broeck sculpsit or A. van den Broeck fecit (or sculpsit).
Text on versos of maps.
Available also through the Library of Congress Web site as a raster image.
AACR2: 100; 630/1; 700/1 ga00
William of Tyre has always been considered one of the greatest medieval writers. An archbishop of Tyre, he grew up in Jerusalem at the height of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, which had been established in 1099 after the First Crusade, and spent twenty years studying the liberal arts and canon law in the universities of Europe. in In 1165, King Amalric made him an ambassador to the Byzantine Empire. After Amalric's death, William became chancellor and archbishop of Tyre, two of the highest offices in the kingdom, and in 1179 he led the eastern delegation to the Third Council of the Lateran. William wrote an account of the Lateran Council and a history of the Islamic states from the time of Muhammad. Neither work survives. He is famous today as the author of a history of the Kingdom of Jerusalem. William composed his chronicle in excellent Latin for his time, with numerous quotations from classical literature. The chronicle is sometimes given the title Historia rerum in partibus transmarinis gestarum ("History of Deeds Done Beyond the Sea") or Historia Ierosolimitana ("History of Jerusalem"), or the Historia for short. It was translated into French soon after his death, and thereafter into numerous other languages. He is considered the greatest chronicler of the crusades, and one of the best authors of the Middle Ages.
Ancient Maps from the Library of Congress. 13th -18th Century Maps.
In the 17th century, maps took a huge leap forward. Mathematical and astronomical knowledge necessary to make accurate measurements had evolved. English mathematicians had perfected triangulation: navigation and surveying by right-angled triangles. Triangulation allowed navigators to set accurate courses and produced accurate land surveys. Seamen learned to correct their compasses for declination and had determined the existence of annual compass variation. Latitude determination was greatly improved with the John Davis quadrant. The measurement of distance sailed at sea was improved by another English invention, the common log. Longitudinal distance between Europe and Québec was determined by solar and lunar eclipses by the Jesuit Bressani in the 1640s and by Jean Deshayes in 1686. With accurate surveys in Europe, the grid of the modern map began to take shape.
The Dutch Golden Age was a period from 1581 to 1672, when the Netherlands experienced the "Dutch Miracle", transcended to the foremost maritime and economic power. In 1568, the Seven Provinces started a rebellion against Philip II of Spain, leading to the Eighty Years' War with Spain and the Thirty Years' War between other European superpowers. Protestants moved from the southern to the northern Netherlands, many settled in Amsterdam, transforming a port town into one of the most important commercial centers in the world by 1630. In addition to the migration of Protestants, there were also influxes of refugees who had previously fled from religious persecution, particularly Sephardi Jews from Portugal and Spain, and Protestants from France. Catholics moved in the other direction - to the southern provinces, modern Belgium. North quickly gained the highest literacy rates in Europe, an abundance of capital, the largest merchant fleet in Europe. The Dutch dominated trade in the Baltic Sea, between China and Japan, and with the English colonies in North America. The Dutch East India Company (VOC) was the first multinational corporation, financed by shares that established the first modern stock exchange. The Bank of Amsterdam, the first central bank, was established in 1609. The Dutch Golden Age is the art period dominanted by Rembrandt, Vermeer, Jacob van Ruisdael, and Frans Hals. Some notable artistic styles and trends include Haarlem Mannerism, Utrecht Caravaggism, the School of Delft, the Leiden fijnschilders, and Dutch classicism. 1672 is called a disaster year" when the Dutch Republic was attacked by England, France, Münster, and Bavaria. The invading armies quickly defeated most of the Dutch States Army and conquered part of the Republic.
Collection - Kingdom of Jerusalem
Chronicler of the Crusades by William of Tyre.Collection - Ancient Maps, Library of Congress
Ancient Maps from the Library of Congress. 13th -18th Century Maps.Collection - XVII Century Maps
Birth of modern maps.Collection - Dutch Golden Age
Dutch Golden Age Prints and Painting: Still life, Landscape, and Genre Art.
Tags
Date
Contributors
Source
Copyright info













































